Top 5 Cybersecurity Threats eCommerce Websites Should Watch Out For
Top 5 Cybersecurity Threats eCommerce Websites Should Watch Out For
The onrush of the retail industry has made e-commerce websites bonne bouches for spammers, hackers, and cybercriminals of all shades trying to make money out of reckless business owners and deceivable consumers. With hackers’ techniques becoming both more advanced and destructive and cybercrime growing exponentially, businesses must do everything possible to protect their assets against attacks.
It doesn’t matter how good your website is and how long you are in the market, your reputation, customers’ trust, and financial foundation can be ruined due to a simple DDoS attack or SQL-injection. Even a single vulnerability can lead to incommensurable damage.
E-commerce security should be among the main challenges and a matter of the greatest concern for business owners. As far as the development of every defensive strategy begins with a clear insight into what has to be fought, knowing the major security threat will help online entrepreneurs repel an aggressor and minimize the consequences of cyber-attacks, if any.
How Can You Suspect That Your E-commerce Site Has Been Hacked?
As a business owner, you probably track users’ activity monitoring the key metrics. If, say, you’ve noticed a sudden downward in sales, don’t hurry to link this fact to a seasonal demand drop. The cause may lie in the consequences of a cyber-attack. However, the sales downturn is not the only sign that indicates that your website has been hacked. Among the most common hints to look out for:
The appearance of strange content
A warning message appears on your site saying it contains malware. This means your visitors may get a notification when accessing your site
The products that haven’t enlisted appear on the website
Your website performance is poor
An increase in the number of errors related to form submissions
Your customers complain about paying for a product, but you didn’t receive their payment.
Your site is blacklisted in Google catalogs
You’ve noticed malicious ads popping up on your store website
Your emails are sent to the SPAM folder
A suspicious server process behavior within that environment that you can’t explain
You’ve noticed an unusual connection to the CPanel from a strange IP from the system logs.
The Most Common E-commerce Cybersecurity Issues That Can Ruin Your Site?
Common examples of e-commerce security threats include data breaches, hacking, monetary theft, phishing, credit card fraud, unprotected provision of services. However, we will touch on five of the most common ones that often plague retail and e-commerce businesses.
DDoS Attacks
Some business owners find Denial-of-service attack (DDoS) nonsensical and don’t treat it seriously. However, the consequences of this attack can be devastating. Ignoring the threat may translate into millions of dollars in lost revenue for every hour of downtime, not to mention the damaged reputation of the affected company. Moreover, in some cases, DDoS attacks can be a cover-up for data breaches. They are often just a distraction: while an IT team is going into resolving a denial of service attack, hackers can steal data. According to a Kaspersky Lab’s report, about 26% of DDoS attacks result in sensitive data loss.
DDoS attacks aim to disrupt the servers by flooding them with an enormous amount of TCP, UDP, HTTP packets making them unable to serve legitimate requests. Hackers often execute massive scale attacks by leveraging a botnet, which is a group of hijacked devices controlled with command software.
The recent DDoS attack occurred in 2020, during the COVID pandemic. Lieferando, the German food delivery service, has become a victim of the threat. Once hackers crippled their server, they couldn’t process orders and had to return money to their customers. The cybercriminals were demanding two bitcoins (around $11,000) to stop the siege. Jitse Groen, the founder of the food delivery service, posted on Twitter about the incident with the attacker’s demand as shown below.
A #ddos attack on a food delivery website @takeaway in the middle of a public health crisis. I hope you sleep well at night. @thuisbezorgd @lieferando @pysznepl pic.twitter.com/YMwSJUOoJn
— Jitse Groen (@jitsegroen) March 18, 2020
Establishing strong DDoS protection is a must for every online business. The common protection techniques include:
Data backups
Minimizing the attack surface area by restricting traffic and placing resources behind CDN’s or Load Balancers.
Using firewalls or ACLs to monitor the traffic and restrict suspicious locations or IPs.
Implementing smart DNS resolution services or CDNs.
SQL-Injections
SQL-injections are specific hackers’ techniques aimed at cracking a website’s database. ASP and PHP applications are bonne bouche for SQL-injections due to the prevalence of older interfaces. Cybercriminals leverage loopholes in back-end coding to insert malicious code included in a query. Once the malicious code executed the SQL-commands, the hackers can gain complete control over the infected website. A successful attack can enable the intruders to gain administrative privileges, extract and disclose sensitive data, manipulate transactions, force identities, and delete database content.
There are 3 rooms for SQL-injections to penetrate your e-commerce website:
Known bugs in third-party modules. To fix the issue, you need to install security patches as soon as they become available.
Known bugs in a platform. To minimize the threat, you need to keep your system updated to its latest version. For instance, Magento, one of the top e-commerce platforms, releases updates for its second version every three months.
Security flaws in custom code. The work of a careless developer can cause vulnerabilities in custom code. Carrying out regular security checks with automated testing tools can help identify and fix these bugs. If your e-commerce website runs on such a sophisticated platform as Magento, you may want to consult with security professionals to scan and fix potential vulnerabilities. [Magento Developers]
Ransomware
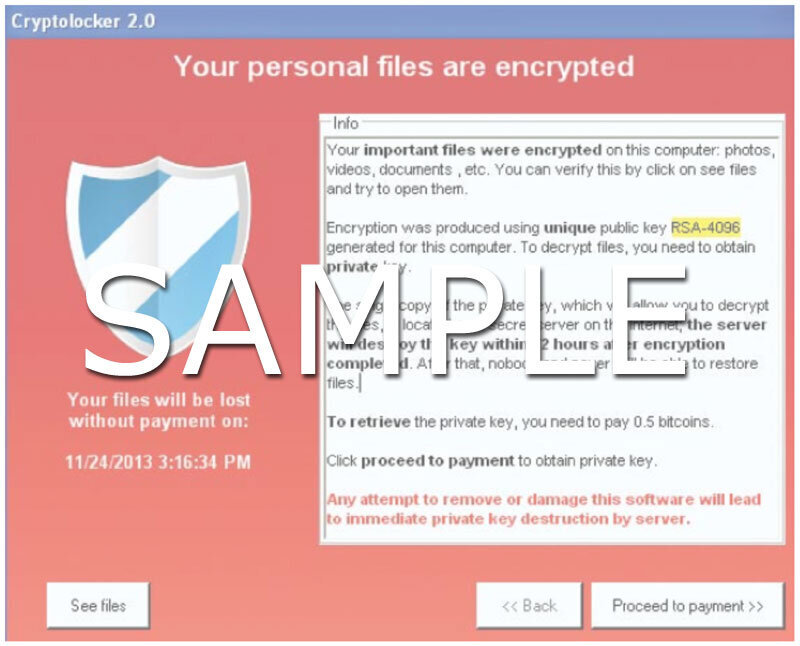
Ransomware is a kind of financial fraud that turned out to be a full-scale business model for ill-minded people. According to new data, ransomware has overtaken credit card theft as the top form of cybercrime. Almost 1 in 5 incidents in 2019 involved this type of attack, where companies of all sizes found their environments compromised by network encrypting malware and faced a demand from attackers to regain access to the data. Below you can see a CryptoLocker ransomware warning appeared to many infected devices.
A Sample Screenshot of Cryptolocker 2.0
Ransomware attacks don’t require solid coding skills and quite easy to perform, so that the number of e-commerce companies affected is increasing exponentially.
There are two ways for ransomware to spread:
Via phishing emails
By visiting an infected website.
Data recovery can be both an expensive and challenging process. Some companies help ransomware victims restore files and data without having to pay the ransom. For example, the nomoreransom.org project helps to prevent the threat and recover the data providing a repository of applications and keys used to decrypt data locked by different types of malware such as ZORAB, REDRUM, MAPO, JAVALOCKER, DRAGONCYBER, and others.
However, the bad news is that in many cases, once the malicious code has been deployed into your device, there is very little you can do.
But there are a few things online entrepreneurs can do to prevent the threat:
Regular backups
Using robust antivirus software and keeping it up to date
Enabling the ‘Show file extensions’ option in the Windows settings on your computer
Proper employee education.
Malicious Bots
Bad bots are self-propagating software that is created to carry out specific tasks and report the information to their botmaster. E-commerce and online retail are constant targets of malicious bot attacks. The bots are often responsible for web scraping, credential stuffing, spam, large scale DDoS attacks, account takeovers, fake account creation, inventory abuse, gift card fraud, and other malicious activities.
Regardless of their type, bots act in the same way: they are scanning a website for security loopholes and leverage them to perform a fraudulent activity or report this security-related information to the botmaster. The last generation of bots professionally mimic human behavior and acting slowly so that their activity rarely raises suspicion.
Considering this, protecting an e-commerce website against bad bots should be an integral part of your security checklist. Online store owners can apply some methods to ensure sufficient protection:
Installing a server firewall to block illegitimate traffic.
Setting up firewall rules for NGINX to determine which types of packets are allowed to go through a firewall and which are not.
Using Cloudflare or another reverse proxy with a built-in bot management tool.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
XSS attacks are among the most common threats for websites using OpenCart, WordPress, and Prestashop plugins. The threat is so crucial that Google is ready to pay a $10, 000 reward to the developer who will be able to find an XSS bug in Google Cloud, Google-developed apps and extensions, or some of their hardware devices (onHub, Home, Nest).
Unlike SQL-injections that harm a server, XSS attacks pose a threat to the users of the infected web resource. The scheme is the following: a victim downloads a page with a JS file with malicious code embedded. Once the script is installed in the system, it begins to steal data from the browser. A hacker can use different tricks to convince the victim to download the infected webpage. For example, they can send an email from a hosting provider that will look like an official one asking to check the account settings. As soon as the attacker gets access to the admin’s cookies, they can control the website panel.
Even the giants with millions of dollars invested in security are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Big companies like eBay, or domestic or international online shopping website, has been victimized by a large scale XSS attacks. The cybercriminals exploited the common vulnerability to inject malicious JS into several listings for cheap smartphones.
Summary
It is hardly an exaggeration to say that the e-commerce industry is in the midst of a cyber arms race. While business owners use modern technologies to improve the user experience, hackers leverage them to make their strategies more advanced. Businesses should put as much effort into protecting their online stores from cyberattacks as they do in driving their businesses.
Reference
Related Articles:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Alex Husar
Alex Husar, a CTO at Onilab with 8+ years of experience in Magento and Salesforce. He graduated from Czech Technical University and obtained a bachelor’s degree in Computer Software Engineering. Alex’s expertise includes both full-stack dev skills and a strong ability to provide project-critical guidance to the whole team.
You can reach out to him: https://www.linkedin.com/in/alex-husar